Choosing a file format
Graphics file formats differ in the way they represent image data (as pixels or vectors), and support different compression techniques and Photoshop features. To preserve all Photoshop features (layers, effects, masks, and so on), save a copy of your image in Photoshop format (PSD).
Like most file formats, PSD supports files up to 2 GB in size. For files larger than 2 GB, save in Large Document Format (PSB), Photoshop Raw (flattened image only), TIFF (up to 4 GB), or DICOM format.

The standard bit depth for images is 8 bits per channel. To achieve greater dynamic range with 16- or 32-bit images, use the following formats:
Formats for 16-bit images (requires Save As command)
Photoshop, Large Document Format (PSB), Cineon, DICOM, IFF, JPEG, JPEG 2000, Photoshop PDF, Photoshop Raw, PNG, Portable Bit Map, and TIFF.
Note:
The Save For Web & Devices command automatically converts 16-bit images to 8-bit.
Formats for 32-bit images (requires Save As command)
Photoshop, Large Document Format (PSB), OpenEXR, Portable Bitmap, Radiance, and TIFF.

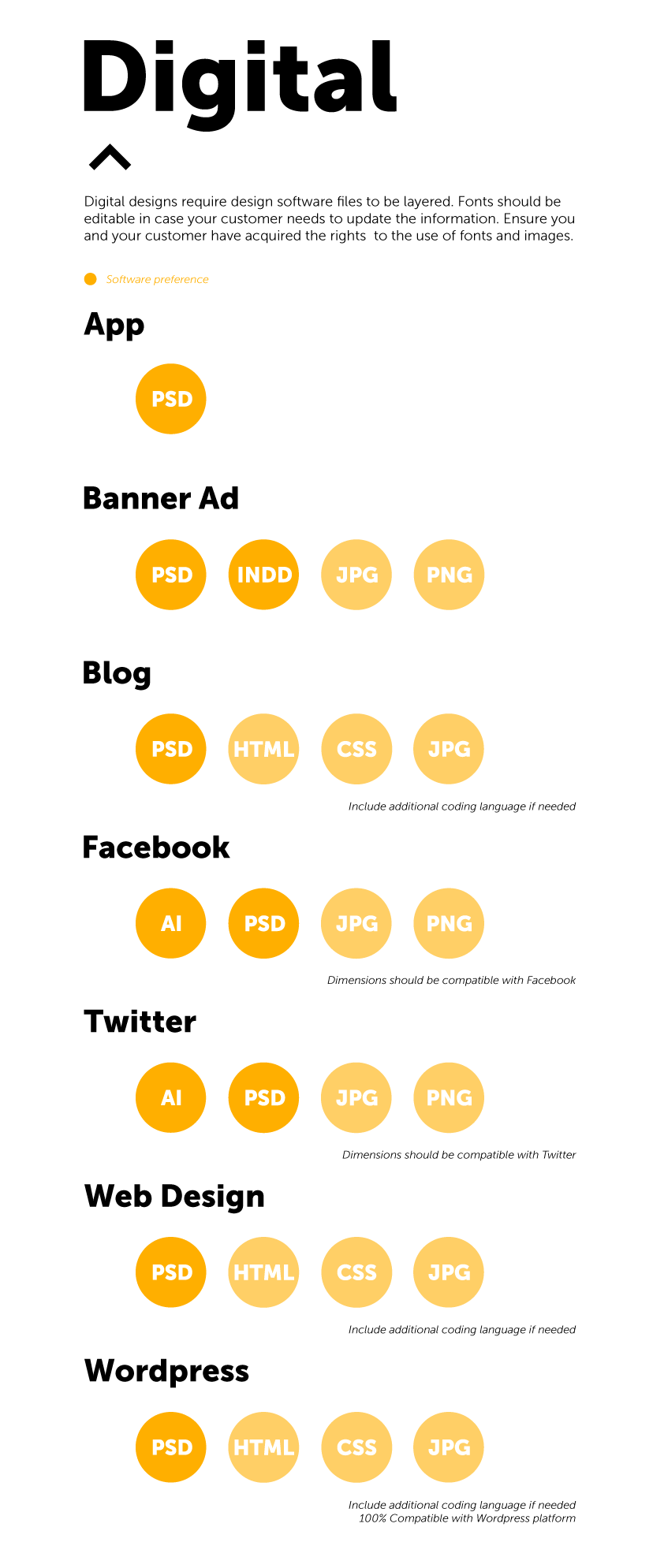
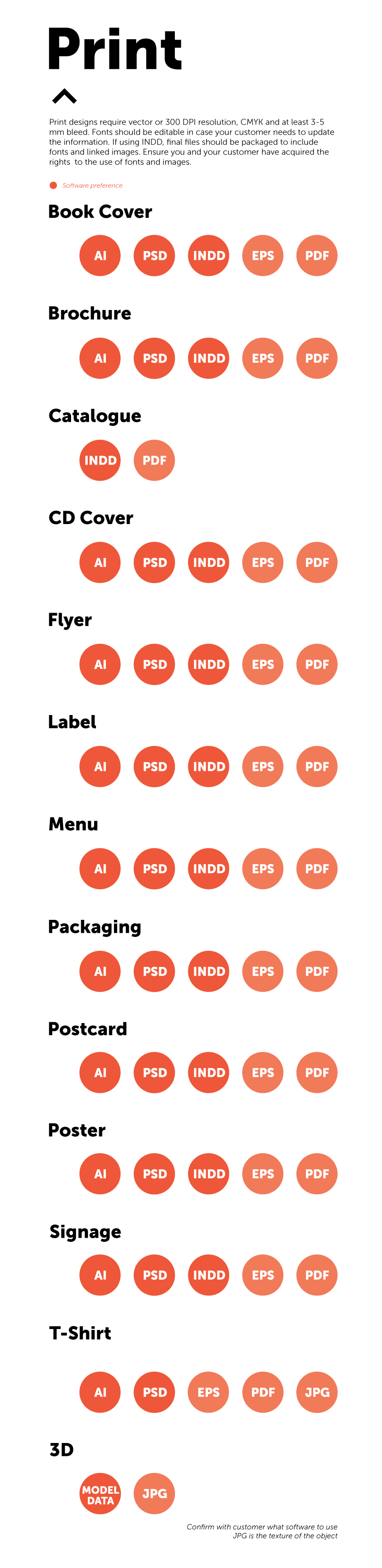
What are source files?
Source files are the files you, the designer, have used to create your designs. The more well-known files include Adobe’s Photoshop, Illustrator and Indesign. These files should be provided to clients so they can print scalable versions of the design or edit them as they see fit.